3 Essential tips for using data driven instruction
What is data driven instruction?
Data driven instruction is an educational approach where you assess your students during a lesson, and let the data that you collect become the guide for teaching and learning in your classroom. You can use a variety of formative assessments and checks for understanding specifically designed to monitor student learning. Students get immediate, individualized feedback, while you get information on class-wide trends in misconceptions that you can clear up in real time. Transformational learning happens when teachers not only use data in their planning but also actively collect data during class and use those learning results to inform their instruction. Keep reading to explore tips for using data driven teaching in your classroom.
Why is data driven instruction important?
Using data to drive instruction helps educators prioritize students’ individual needs, and its results are backed by science. A research study from Bertram Opitz on delayed and immediate feedback found that immediate feedback has a significantly larger increase in learning than delayed feedback. Additionally, one group of researchers who conducted a meta-analysis on the effects of feedback on learning went as far as to say that “delaying feedback has a negative impact on learning outcomes,” underlining the power of giving cues at the moment to students.
What tool can I use for data driven instruction?
When using data to inform instruction, I love using digital tools because of how quickly I can gather student input; the more immediate data I have, the better I can guide my students toward success. With so many ways to collect formative assessments, Nearpod is the ideal tool to collect student data and act on it. With nine types of formative assessment tools, you can choose which combination of assessments work best for you and your students.
Nearpod gives you the ability to create interactive slide-based lessons and videos where you can embed assessments and activities to check for student understanding in real time. This makes it even easier to collect data to provide immediate feedback to students. With tools like Polls, Quizzes, Open-Ended Questions, and their gamified quiz called Time to Climb, teachers can easily access their students’ learning data while also keeping them engaged, focused, and participating.
New to Nearpod? Sign up to access formative assessment tools and create interactive lessons!
3 Essential tips for using data driven instruction
1. Planning is key for data based instruction
Data driven instruction in the classroom begins with planning. During planning, teachers design classwork to test student knowledge and create a plan for giving feedback.
Planning for teaching using examples of data driven instruction includes the following:
- Crafting an answer key
- Labeling the standards aligned to each question
- Deciding what questions you’ll give feedback on and when you’ll give it
Some teachers create tracking tools to help them keep track of student data. Seating charts can often double as trackers. Teachers can write down which questions students are getting wrong. They often use symbols (like stars, circles, squares, etc) to track more nuanced differences like procedural vs. conceptual errors. Another way to structure a tracker is according to standard, skill, or question type with room to record students’ names.
If you’re using Nearpod, explore valuable formative assessment options and select the activities that fit best for the topic, student, and you as the teacher. Also, keep in mind that you automatically have access to students’ responses in real-time. You can also visit all data and insights collected from the lesson in the post-session reports. Allocate time in your lesson for addressing misconceptions at the moment for students.
2. Use formative assessment tools
While writing questions and planning opportunities for feedback are unique to each teacher, it’s important to simplify tracking and responding to student data. Teachers can use checks for understanding to get a more immediate gauge of how an entire class is thinking. These include voting with your hands, turning and talking, using whiteboards, polling, and more. While it’s common to quiz students using handouts or sheets of paper, collecting actionable feedback from each student can be tedious and manual. By using technology, teachers can save time with collecting data and instead focus more on their instruction and connecting with students.
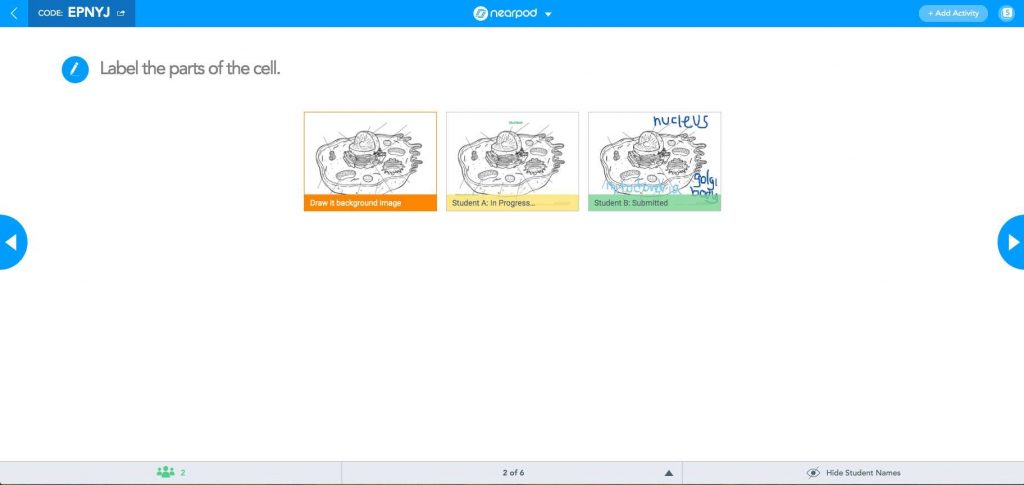
Using Nearpod’s formative assessments like Open-Ended Questions, Multiple-Choice Quizzes, Time to Climb, Draw it, and more interactive activities, student data arrives on your screen in a clean, alphabetical list. You get clear and organized responses in real time so that you can highlight strong responses and address misconceptions. For deeper reflection on using data driven instruction, teachers can print out post-session reports from an individual student or the class as a whole to review data points. This is especially important when prepping for standardized tests. Although learning is more than test scores, identifying areas where students need extra support, can be accomplished through teacher-led differentiation using data.
In my science classroom, I love to use Polls and Open-Ended Questions to gather student hypotheses before we observe a chemical reaction and after each experiment to evaluate the accuracy with which students interpreted their results.
3. Give effective student feedback
What does valuable feedback look like, and how do you use data to drive instruction? The acronym SUGAR can help you make your feedback high-impact and high-quality for students. After analyzing data, use your insights when lesson planning a data driven reteach for your class.
SUGAR stands for:
- Small: Feedback is small when it is something you can deliver quickly and something a student can fix quickly. This allows you to give feedback to as many students as possible.
- Urgent: Urgent feedback addresses the most pressing concerns, avoiding off-topic.
- Generalize: Generalized feedback is transferable and focuses on a pattern of errors as opposed to one error in a specific question.
- Actionable: The feedback has actionable, clear, and observable steps the student could use to fix the error.
- Return: This ensures that after a teacher gives feedback, they return to follow up with the student to validate or push further.
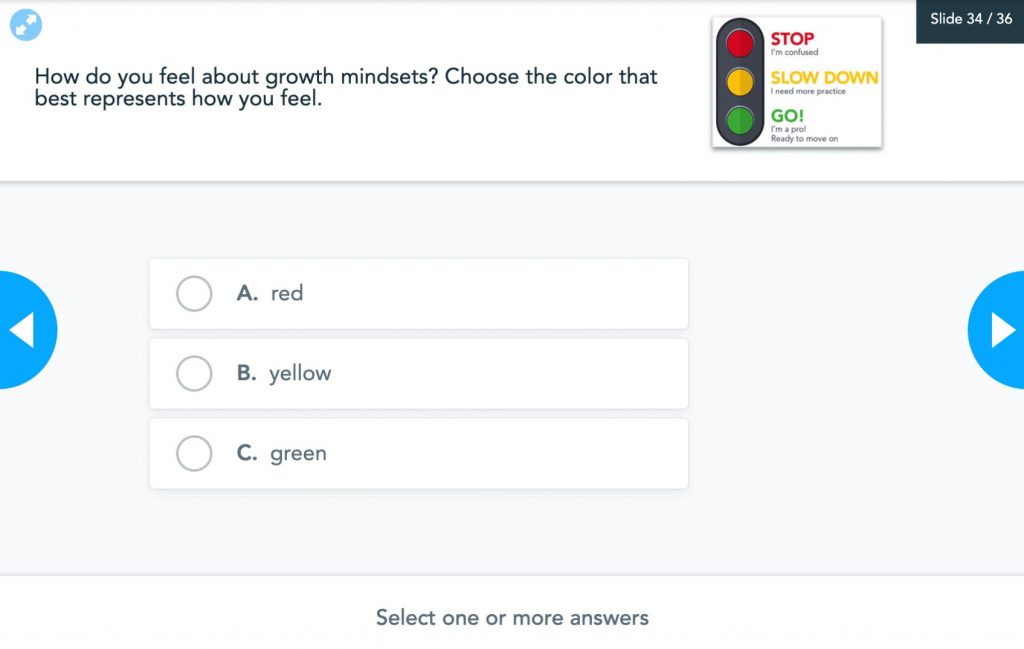
It’s important to consider students’ social and emotional well-being when providing feedback as well. To encourage learning, we must create an environment that accepts a growth mindset and empowers all students. Not all feedback is executed the same, and your relationship with your students should always be at the center.
Start implementing data driven instruction today
Feedback and using data to drive instruction can transform your classroom. As you give more frequent and meaningful information you give to your students, they’ll become more confident and more in control of their academic journey. Using frequent checks for understanding with your students in any grade level, you can see how cohesive and constructive feedback empowers students to take ownership of their learning.
Through these tips, you’ll be planning using data driven strategies in no time. If you need extra support, Nearpod is always here to help.
New to Nearpod? Sign up to access formative assessment tools and create interactive lessons!

Nearpod’s award-winning platform is used by thousands of schools around the globe, transforming classroom engagement.