Tips for teaching AI literacy with confidence in schools
AI literacy is the ability to understand, evaluate, and responsibly interact with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. For students, it means not just knowing how to use AI-powered tools but also grasping how these systems function, the ethical challenges they raise, and how they impact society at large. As AI shapes the way we live, learn, and work, building a strong foundation in AI literacy empowers students to navigate technology with confidence and integrity.
Why is teaching AI literacy in schools important?
Building AI literacy in schools cultivates a culture of curiosity, critical thinking, and responsibility. It equips students to not only use technology but also understand how AI works, how it shapes society, and how to engage with it ethically. AI is changing and evolving, just as social media did, so it’s important for educators and students to be informed.
AI literacy blends technical understanding with media literacy, ethical awareness, and problem-solving. It empowers students to become informed users, creators, and decision makers in a world increasingly influenced by AI.
To do this effectively, educators must introduce key concepts such as algorithmic bias, data privacy, and responsible AI use—drawing on frameworks such as the AI Literacy Act and AI4K12’s “Five Big Ideas.” Additionally, embedding AI literacy into education aligns with broader goals of preparing students for future careers and civic life. It ensures they are ready to navigate and shape an AI-driven world with confidence and integrity. By integrating AI digital literacy into modern education, schools not only keep pace with technological evolution—they lead it.
Nearpod & Common Sense: Ready-to-teach AI literacy lessons
Navigating AI’s evolution and complexities could be a full-time job in and of itself. Headlines each week claim new benchmarks and new innovations we never thought possible. Speed of change shouldn’t deter us from teaching kids the fundamentals of AI, though. And thankfully, educators don’t need to be experts or journalists to understand how to teach kids about AI.
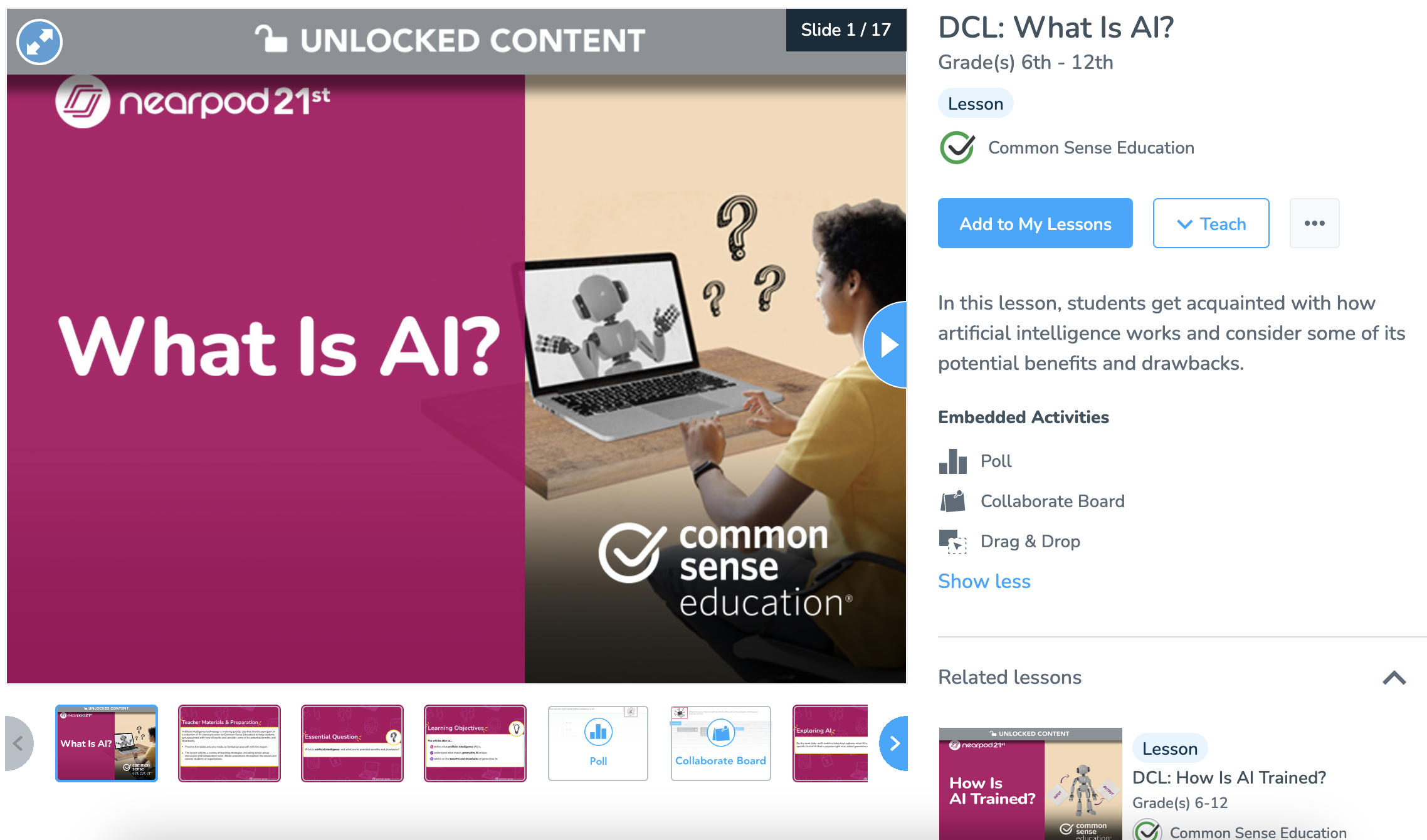
Nearpod’s 21st Century Readiness Program offers interactive AI literacy lessons, developed in partnership with Common Sense Education. These digital resources help teachers bring AI literacy into the classroom with interactive, ready-to-teach lessons to understand what AI is and how it works, consider the benefits and risks, and think critically about responsible use. Nearpod empowers both teachers and students to build skills on AI literacy in education.
6 Tips for teaching AI literacy in schools with confidence
1. Navigate school and state AI policies
Staying informed about state and school AI guidelines is crucial for effective and responsible AI integration. As of April 2025, more than 28 states provide guidance on AI in education (ECS AI Education Task Forces). Check with your administrator or technology coach for your school’s current AI policy, including approved tools and venues.
Before using an AI tool, consider these key policy and equity points:
- Ensure you are aware of your school’s guidelines and AI-approved tools.
- Review policies for protecting student data and upholding privacy standards.
- Be mindful of equitable access, ensuring all students can benefit from AI-powered learning.
- Stay informed about ongoing conversations on AI literacy frameworks at the local and national levels.
Here are some additional helpful resources:
2. Build awareness and curiosity
AI literacy for students starts with fostering curiosity. Educators can explore how AI operates in daily life, from chatbots to photo filters. The task is to bridge these concepts with what students already know, investigating how tools students encounter—such as recommendation systems on streaming apps —work behind the scenes.
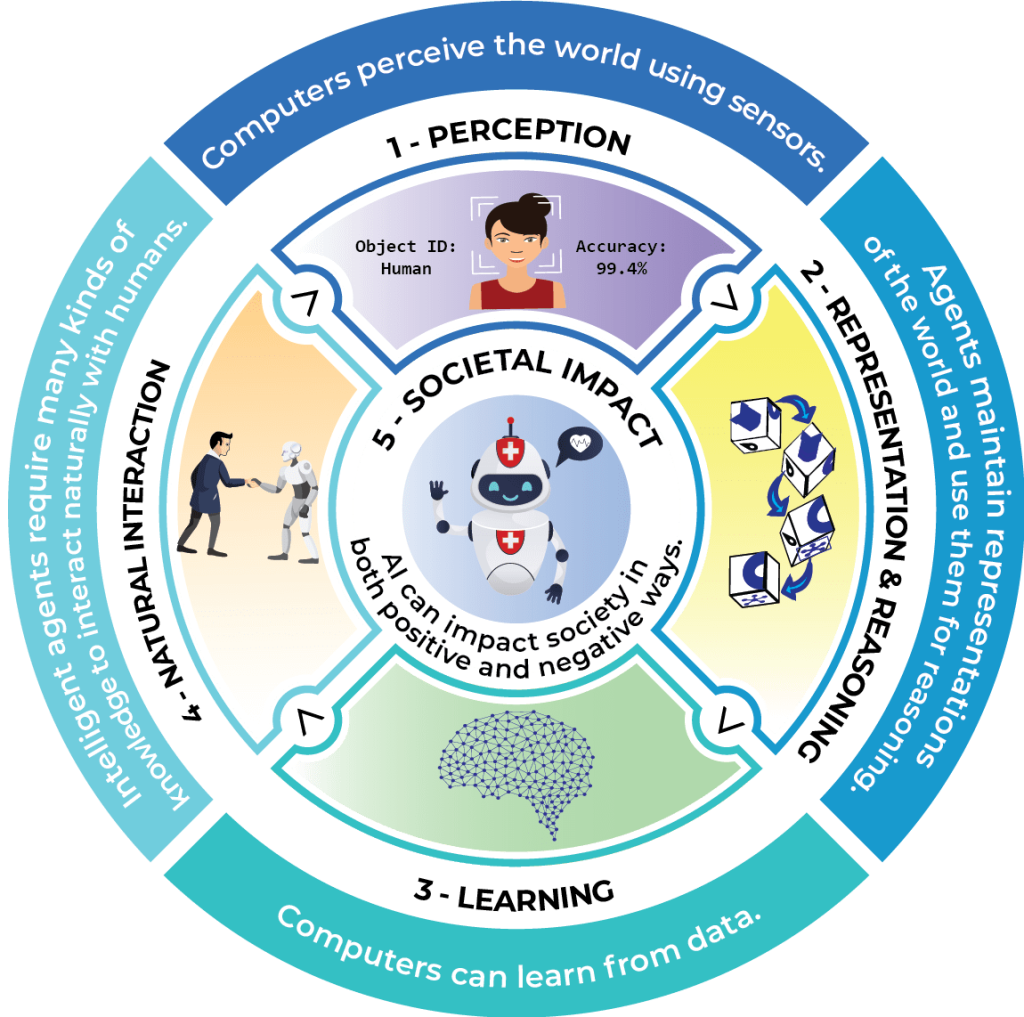
Implement classroom activities that explore perception using the “Five Big Ideas in AI” developed by the AI4K12 initiative. For instance, teachers can ask students to compare how humans perceive the world versus how computers do so through sensors and algorithms powered by machine learning. These activities help develop students’ critical thinking skills about AI’s application in daily routines.
Nearpod’s interactive environment lends itself perfectly to awareness-building discussions. Using Nearpod’s premade lessons on AI, educators can prompt students to explore how AI shapes their interactions with technology and the ethical considerations involved.
Kick off discussions with our “What Is AI?” lesson for grades 6-12. Students will explore how artificial intelligence works and its potential benefits and drawbacks.
3. Teach critical thinking to question AI
Sharpening students’ critical thinking skills when interacting with AI is essential. Generative AI models can produce highly confident-sounding responses riddled with inaccuracies or biases. Thus, students need to learn how to question and verify information.
Incorporate a “Fact-Check Friday” routine, particularly for grades 6–12. Pose questions to AI—like “Can lightning strike the same place twice?”—and have students verify the response using reliable sources. This can evolve into multi-source verification exercises that teach media literacy in alignment with the AI literacy act.
Here’s a structured template to guide students through the process:
- Find a trustworthy source to compare.
- We believe this because…
- We’re not sure because…
- We still want to find out…
- What did we learn? What do we still wonder?
Consider incorporating a Fact-Check Friday into your classroom routine. Start by posing a question to AI, such as “Can lightning strike in the same place?” and have students assess the accuracy of its response. Then, guide them to research reliable sources to verify the information. Through this process, students learn to evaluate AI-generated content and cross-reference multiple sources.
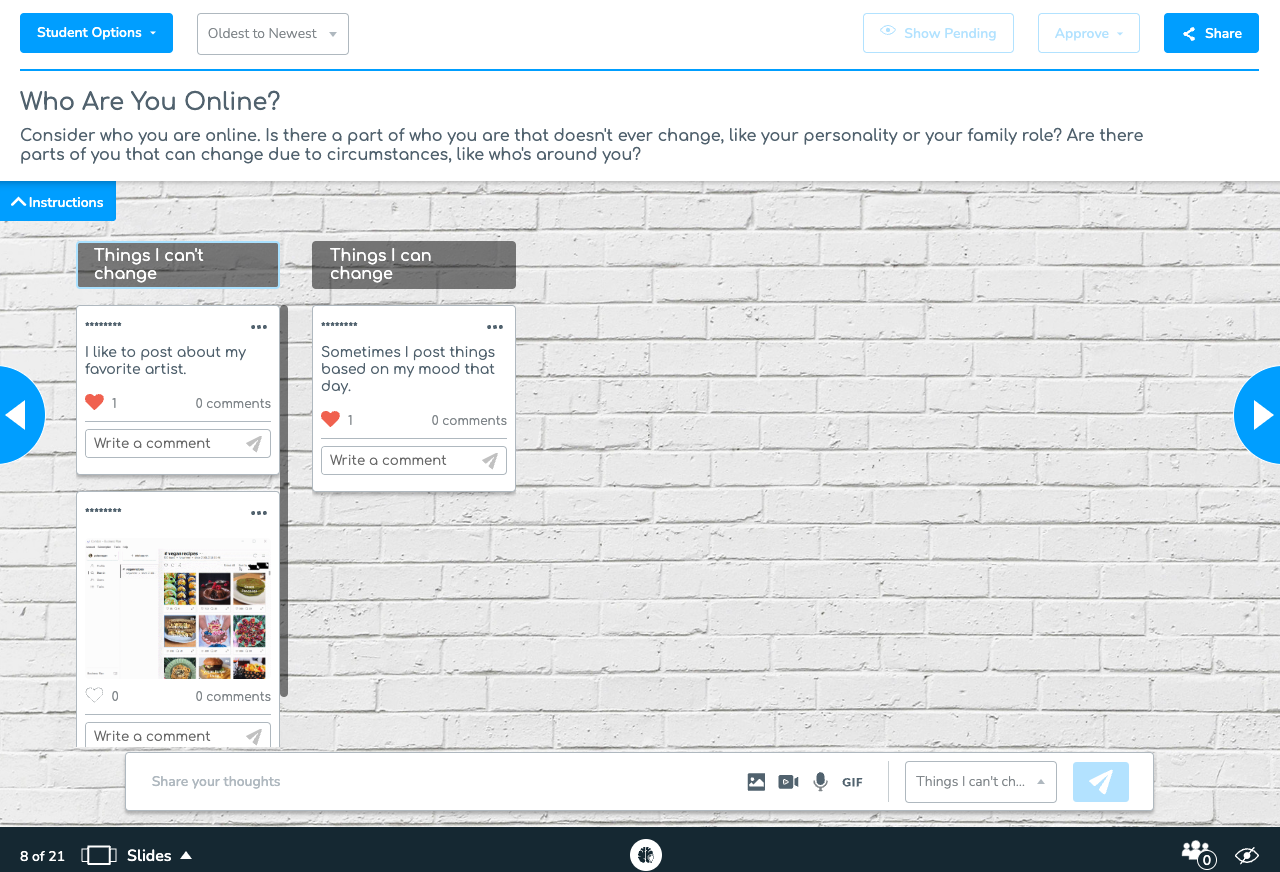
With Nearpod’s interactive tools, teachers can conduct real-time group discussion by using polls or Collaborate Board. Students can share their findings and participate in group discussions on detecting bias and refining AI-generated content.
4. Create safe environments for experimentation
Build a safe environment where students can freely experiment with AI tools and understand their outputs. By modeling positive and careful use of AI tools, you show students how to explore, question, and learn from technology while maintaining ethical standards. Clearly explain which platforms are permitted, how students should use them, and what responsible AI interaction looks like.
Start by leading the class through a prompt and the output to introduce concepts to model responsible use and critical thinking. Then, consider doing the following activities.
Example 1: AI Moment Mondays
Dedicate a short weekly session to experimenting with AI tools as part of regular routines. For instance, challenge students to write a poem with an AI or test how the AI responds to different prompts. Use these sessions to foster discussion about how AI functions, how input affects output, and how to use such tools ethically and transparently. This not only improves technical and critical thinking skills but also raises awareness of the ethical implications of AI in the learning environment.
On Nearpod, add an approved AI tool to the reference media of a Collaborate Board or Draw It. Give your students a problem or question to solve using AI, but do not give them the prompt. Have your students insert their prompt and results into the Nearpod lesson and discuss the various results.
Example 2: Interactive Story Time
Create a class story where students provide initial ideas, then let an AI suggest plot twists or dialogue. Students can discuss and decide which ideas to include, building skills in literacy, creative thinking, and understanding how AI generates output. This collaborative activity helps students distinguish between their contributions and the AI’s input, supporting both digital and critical literacy.
5. Incorporate ethical and responsible AI principles
One of the most important aspects of teaching AI literacy is discussing its limitations and risks. From data privacy concerns to algorithmic bias, students must grasp the ethical implications of AI use.
Hold discussions on responsible AI principles. Educators can guide students through scenarios involving copyright and plagiarism, such as whether AI-generated work constitutes original content. Students should also understand how their data may train AI systems without their knowledge. Additionally, having these conversations within your school community organization fosters a shared understanding of ethical AI use.
Here are some examples educators can share about AI’s risks and limitations:
- Incorrect or misleading responses – AI can provide false information while appearing confident and authoritative
- “AI hallucinations” – When AI generates completely fabricated information that seems plausible
- Bias in AI-generated answers – AI systems can perpetuate existing societal biases and stereotypes
- Copyright infringement risks – AI may plagiarize by reproducing copyrighted material without proper attribution
- Privacy and data security risks – Personal information shared with AI systems may be stored for other uses
With Nearpod, educators can access premade digital citizenship lessons to discuss ethical AI concerns. These lessons help students connect AI ethics to broader digital literacy concepts they already understand, such as online safety and privacy.
For example, use the “Facing Off with Facial Recognition” lesson to guide students through understanding what facial recognition technology is and critically evaluating its benefits and risks in their daily lives. The lesson uses Common Sense Education’s “Take a Stand” thinking routine to help students consider multiple perspectives on this complex digital issue that lacks clear right or wrong answers.
6. Establish clear classroom AI guidelines
For older students, establishing clear guidelines on when and how AI tools are acceptable for assignments is key. This approach not only sets boundaries but also encourages transparency and builds AI literacy skills for students.
Develop an “AI Integration Rubric” to clarify to students when it’s permissible to use AI. Label activities such as brainstorming or proofreading as “AI-appropriate,” while ensuring core learning objectives, like writing structure development, remain AI-free.
Here are classroom learning agreements created by Common Sense Education:
Empower the next generation through AI literacy
Teaching AI literacy in schools is about more than integrating technology; it’s about shaping informed, ethical, and critically thinking individuals. Schools looking to develop and deploy AI literacy programs can leverage platforms like Nearpod, where educators can empower students today to lead responsibly tomorrow.
Start small by labeling everyday technologies or try platform-specific solutions to integrate AI literacy into your curriculum—whatever your approach, the impact will be profound. Lead the charge in preparing students for AI-powered futures by making AI literacy a central pillar in your classrooms.

With 20+ years in educational technology, Julianne Robar’s work has centered on intelligent systems that integrate assessment, practice, instruction, and standards to transform student data into actionable insights. She believes effective AI in education connects data across products to help teachers identify student growth opportunities with greater precision.
Jennifer Ehehalt is a seasoned educator with over 20 years of experience, formerly an elementary teacher who now designs and delivers impactful professional development for educators nationwide. She specializes in onboarding school districts and crafting customized implementation plans that promote digital literacy, wellness, and positive school culture through technology.